Excel is an extremely powerful program used by businesses all over the world. Users with advanced Excel skills are in huge demand.
If you are wondering “how to improve my Excel skills?”, you are in the right place. The list below is a collection of advanced Excel tips to enhance Excel skills and make you an Excel superhero.
Advanced Excel Formulas
If you asked someone, what are advanced Excel skills? You can be sure that advanced Excel formulas would be a common response.
Formulas are what drive an Excel spreadsheet. Formulas provide the muscle for a spreadsheet to analyse, manipulate, convert and look up data with incredible speed and power.
An advanced Excel user would need advanced formula skills. They would have a commonly used list of functions that they know well, but also the skills and confidence to adapt to any situation requiring formulas.
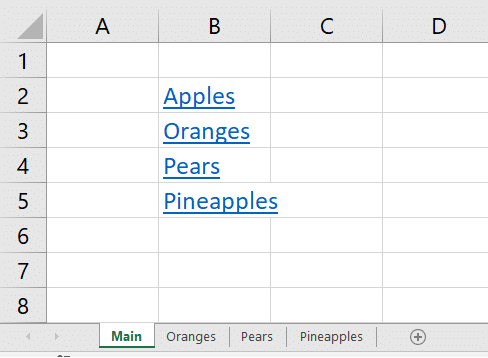
Ultimate VLOOKUP function guide
5 examples of the groovy SUMPRODUCT function
The INDIRECT function – 5 great examples
4 alternatives to nested IF formulas
Learn more advanced Excel formulas
[Read more…] about Advanced Excel Skills